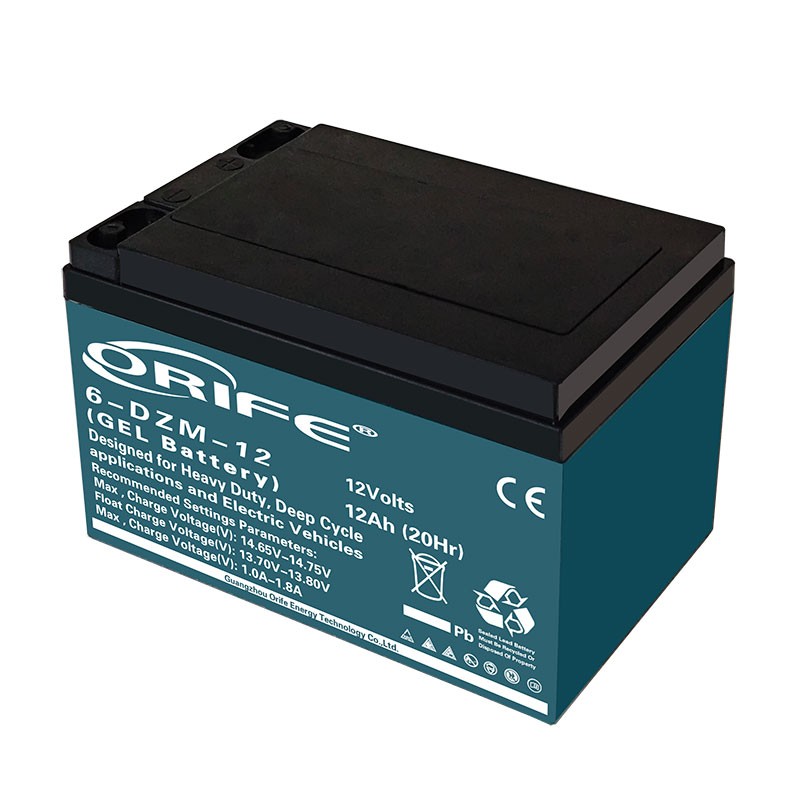
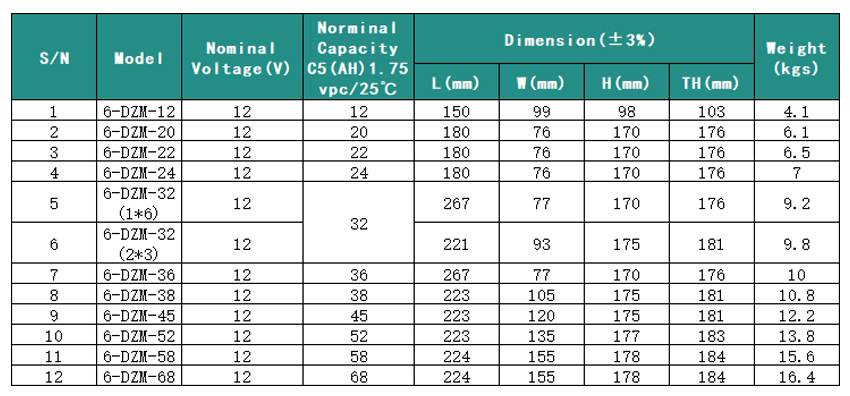
6-DZM-12 Ebike Battery
- Category: Ebike battery
- Capacity : 12V12AH
- Dimension : 150*99*98*103mm
- Cycle times : 600 times 80% DOD
- Weight : 4.1kgs
Electric vehicle battery (EVB) is a battery used in a pure electric vehicle (BEV) or hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) to supply energy to the electric motor. Most are rechargeable batteries, electric vehicle batteries will generally be designed for high capacity, with large ampere-hour (or kilowatt · hour) specifications.
Electric vehicle batteries are different from the car batteries that are responsible for starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) in ordinary vehicles. Electric vehicle batteries need to be able to continue to have power output for a long time, which is a deep cycle battery that needs to output a considerable degree of electricity. The electric vehicle battery is characterized by its high power to weight ratio, specific energy and energy density: if the electric vehicle battery is light, the car weight will be relatively light, which can improve the performance of the vehicle, so it is generally hoped that the weight of the electric vehicle battery can be relatively light. Compared to liquid fuel, the specific energy of most EV batteries is still too low, which also limits the maximum horsepower range for vehicle electrification. Vehicles with large mileage to a certain extent may not be able to be converted to electric vehicles due to weight issues.
Lead-acid batteries are the cheapest electric vehicle batteries and were previously the most common electric vehicle batteries. Lead-acid batteries can be divided into two types: the batteries responsible for starting the ignition of the vehicle engine (car batteries), and deep cycle batteries. Car batteries are designed to use only part of their power to provide a large discharge current to start the engine, while deep-cycle batteries are a continuous supply of batteries to keep electric vehicles (such as forklifts or golf carts) running. Deep-cycle batteries are also used as auxiliary batteries in recreational vehicles, but require multiple stages of charging. When the lead-acid battery is discharged, the power can not be reduced to less than 50% of its capacity, if the power is too low, it will reduce its life. Lead-acid batteries require regular inspection of the electrodes and electrolyte, and occasionally need to replenish the electrolyte.
Since lead-acid batteries are mature technology, easy to obtain, and low in price, early electric vehicles almost all use lead-acid batteries.
The weight of lead-acid batteries in electric vehicle applications is about 25-50% of the total weight of the vehicle. Lead-acid batteries have lower specific energy than fossil fuels. At first, this difference is less obvious because electric cars have lighter drivetrains, even if the best batteries (and therefore heavier) are used in ordinary vehicles. The efficiency of current deep-cycle batteries (70-75%) and stored power will decrease at lower temperatures, and the heating coil will reduce the efficiency and battery mileage by up to 40%.
The charging and operation of lead-acid batteries release hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur, which are naturally occurring substances that are generally harmless if properly ventilated.
INQUIRY
CATEGORIES
CONTACT US
Name: Catherine zhong
Mobile:+86 18802012393
Tel:+86 18802012393
Whatsapp:+86 18802012393
Email:catherine@orifeenergy.com
Add:311, Building 3, 11 Dalingshan Road Guangzhou, Guangdong, China









